Into the wild
Solar energy is the energy of the sun that is converted into thermal or electrical energy. Solar energy is the cleanest and most abundant source of renewable energy available. There are three main ways to use solar energy: photovoltaics, solar heating and cooling, and concentrated solar energy. Photovoltaics generates electricity directly from sunlight through electronic processes and can be used to power a variety of electronic devices, from small appliances such as calculators and traffic signs to homes and large commercial enterprises.
off-grid inverter
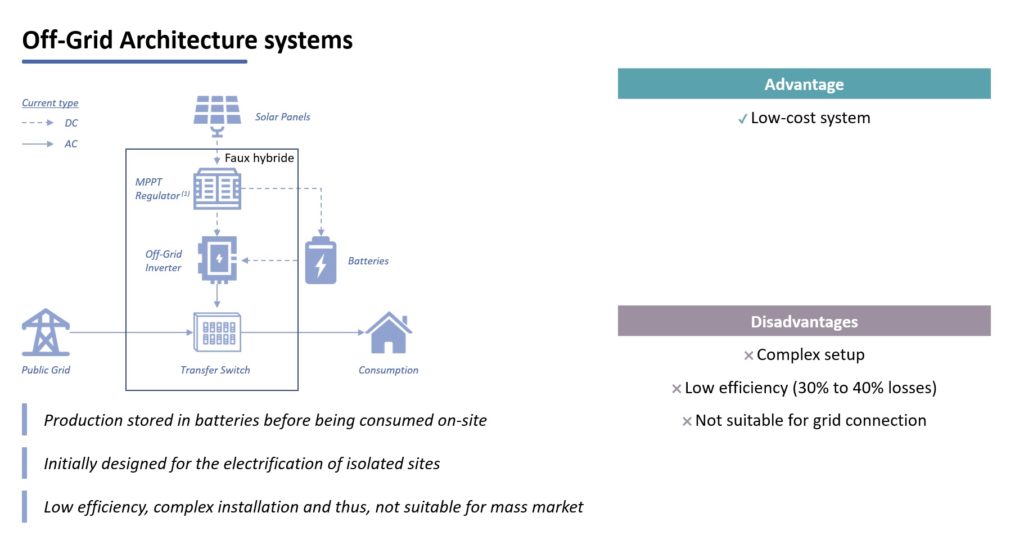
The off-grid inverter is capable of handling solar panels and a solar battery, and as its name suggests, it provides the renewable solar energy to the loads while not being connected to the grid.
An installation of an off-grid system is very different from installation of the on-grid one. The system is usually built using multiple components (solar panels, MPPT charger, battery, inverter) which need to work well with each other but also must be extremally carefully considered to fit the installation site. To give some examples:
- if the solar array is too small with respect to the battery, charging of the latter will take a very long time, or
- if the power output of the off-grid inverter is too low with respect to the loads on the installation site, it will lead to overloads and may even cause equipment damage.
In systems built using off-grid inverter the DC power generated by solar panels is used by a MPPT charger to charge the solar battery. Once the battery is full the off-grid inverter is able to tap into the renewable energy stored in the battery and supply the power to the loads. What is significant, the inverter will not be able to provide renewable power to the loads before the battery is full, which means that if the site requires power while the battery is charging, another power supply, such as a diesel generator, must be used. Moreover, the totality of solar production is being stored in and extracted from the battery which has a severe impact on the overall efficiency of the system, because of several conversion steps on the path from a solar panel to a load. While the solar batteries are obviously meant to be charged and discharged, heavy and frequent cycling will only cause them to expire faster.
Because of the shortcomings of both on-grid and off-grid inverters, a modern device which combines the advantages and addresses the flaws of both technologies had to be designed.
Below is a schematic of a solar installation using Off-Grid :